Note
Click here to download the full example code
Outlier detection via leave-one-out¶
Outliers can sometimes be identified by assessing the influence of each datapoint. To assess the influence of one point, we fit the dataset while the point and compare the result with the fit of the full dataset. The code below shows how to do this with lmfit. Note that the presented method is very basic.
from collections import defaultdict
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import lmfit
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 130
plt.rcParams['figure.autolayout'] = True
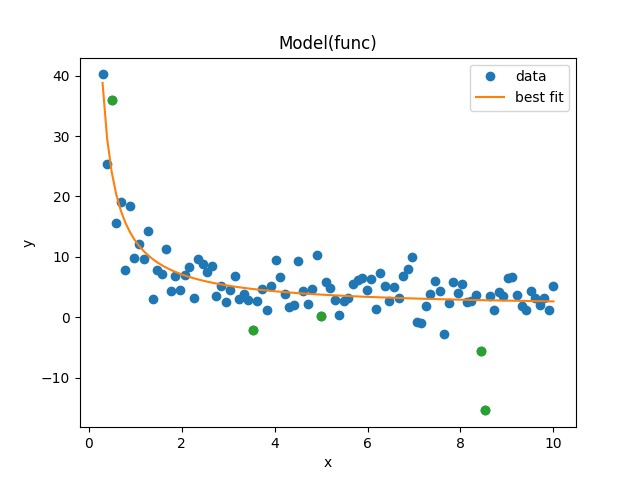
Generate test data and model. Apply the model to the data
x = np.linspace(0.3, 10, 100)
np.random.seed(1)
y = 1.0 / (0.1 * x) + 2.0 + 3 * np.random.randn(x.size)
params = lmfit.Parameters()
params.add_many(('a', 0.1), ('b', 1))
def func(x, a, b):
return 1.0 / (a * x) + b
# Make 5 points outliers
idx = np.random.randint(0, x.size, 5)
y[idx] += 10 * np.random.randn(idx.size)
# Fit the data
model = lmfit.Model(func, independent_vars=['x'])
fit_result = model.fit(y, x=x, a=0.1, b=2)
and gives the plot and fitting results below:
Out:
/Users/Newville/Codes/lmfit-py/examples/example_detect_outliers.py:46: UserWarning: Matplotlib is currently using agg, which is a non-GUI backend, so cannot show the figure.
plt.show()
[[Model]]
Model(func)
[[Fit Statistics]]
# fitting method = leastsq
# function evals = 12
# data points = 100
# variables = 2
chi-square = 1338.34458
reduced chi-square = 13.6565773
Akaike info crit = 263.401856
Bayesian info crit = 268.612196
[[Variables]]
a: 0.08937623 +/- 0.00590168 (6.60%) (init = 0.1)
b: 1.51298994 +/- 0.46229147 (30.55%) (init = 2)
[[Correlations]] (unreported correlations are < 0.100)
C(a, b) = 0.601
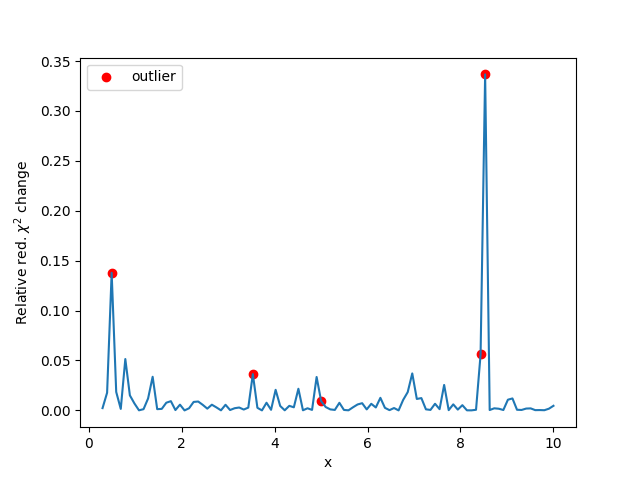
Fit the dataset while omitting one data point
best_vals = defaultdict(lambda: np.zeros(x.size))
stderrs = defaultdict(lambda: np.zeros(x.size))
chi_sq = np.zeros_like(x)
for i in range(x.size):
idx2 = np.arange(0, x.size)
idx2 = np.delete(idx2, i)
tmp_x = x[idx2]
tmp = model.fit(y[idx2],
x=tmp_x,
a=fit_result.params['a'],
b=fit_result.params['b'])
chi_sq[i] = tmp.chisqr
for p in tmp.params:
tpar = tmp.params[p]
best_vals[p][i] = tpar.value
stderrs[p][i] = (tpar.stderr / fit_result.params[p].stderr)
Plot the influence on the red. chisqr of each point
Out:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x1a1fc09090>
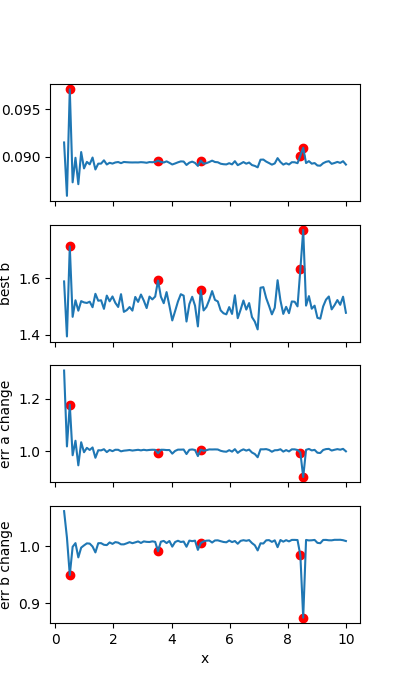
Plot the influence on the parameter value and error of each point
fig, axs = plt.subplots(4, figsize=(4, 7), sharex='col')
axs[0].plot(x, best_vals['a'])
axs[0].scatter(x[idx], best_vals['a'][idx], color='r', label='outlier')
axs[0].set_ylabel('best a')
axs[1].plot(x, best_vals['b'])
axs[1].scatter(x[idx], best_vals['b'][idx], color='r', label='outlier')
axs[1].set_ylabel('best b')
axs[2].plot(x, stderrs['a'])
axs[2].scatter(x[idx], stderrs['a'][idx], color='r', label='outlier')
axs[2].set_ylabel('err a change')
axs[3].plot(x, stderrs['b'])
axs[3].scatter(x[idx], stderrs['b'][idx], color='r', label='outlier')
axs[3].set_ylabel('err b change')
axs[3].set_xlabel('x')
Out:
Text(0.5, 0, 'x')
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.086 seconds)