ipUnidig.adl
This package provides EPICS device support for the Greenspring IP-UD (formerly called the IP-Unidig) series of digital I/O Industry Pack modules. It also supports the Systran DIO316I and the SBS IP-OPTOIO-8. The IP-UD family includes more than 20 separate models, though some are no longer available. This software provides support for most of these models. Most models provide 24 bits, with each bit individually programmable as an input or an output. The last section of this document describes any special features or restrictions on particular models.
The driver is written in C++, and consists of a class that inherits from asynPortDriver, which is part of the EPICS asyn module. The driver supports 3 parameters, identified by the drvInfo strings used in the INP and OUT fields of records: DIGITAL_INPUT, DIGITAL_OUTPUT, and DAC_OUTPUT. DAC_OUTPUT is only supported on the IP-Unidig-HV series of modules.
The driver supports interrupts on input transitions for modules that provide this capability, such as the IP-Unidig-I. Interrupts can be individually enabled and disabled for low-to-high and high-to-low transitions on each input bit. The interrupts can be used for I/O Intr scanning of bi and longin records. They can also be used to call other drivers when an interrupt occurs. This capability is used by the synApps quadEM module. The quadEM VME card cannot generate interrupts, but it can output a TTL pulse each time new data is available, at up to 815 Hz. If this pulse is input to the Ip-Unidig, the ipUnidig interrupt routine will call the quadEM driver each time new data is available.
Most IP-Unidig modules are bi-directional, meaning each bit can be either an input or an output. This is done using open-collector output circuits, with pull-up resistors to +5V. If the output bit is set to 1 (High), then the open-collector transistor is turned off and the signal is pulled up to +5V. In that state an external device can drive the line to 0V or 5V. There is an independent input sensor that measures whether the line is above the TTL threshold (=High=1) or below the TTL threshold (=Low=0). Thus, setting the output 1 (High) effectively enables that line as an input. If the output is set to 0 (Low), its open collector will sink the current through the pull-up resistor and the line will go to 0V, and an external device cannot change the state.
The following lines are needed in the EPICS startup script for the IP-Unidig.
# Initialize Greenspring IP-Unidig
# initIpUnidig(char *portName,
# int carrier,
# int slot,
# int msecPoll,
# int intVec,
# int risingMask,
# int fallingMask)
# portName = name to give this asyn port
# carrier = IPAC carrier number (0, 1, etc.)
# slot = IPAC slot (0,1,2,3, etc.)
# msecPoll = polling time for input bits in msec. Default=100.
# intVec = interrupt vector
# risingMask = mask of bits to generate interrupts on low to high (24 bits)
# fallingMask = mask of bits to generate interrupts on high to low (24 bits)
initIpUnidig("Unidig1", 0, 1, 2000, 116, 0xfffffb, 0xfffffb)
dbLoadTemplate "ipUnidig.substitutions"
Interrupts on the IP-Unidig-I models are fully supported. For each input bit the hardware can be programmed to generate interrupts on rising or falling transitions, or neither. The interrupt service routine software is written to allow alternating which transition generates interrupts, so that it is possible to generate interrupts on both rising and falling transitions.
The risingMask and fallingMask parameters to initIpUnidig are used to specify which bits should generate interrupts on each edge. It is possible to have some bits set in neither mask, some in one mask and not the other, and some specified in both masks. For example if risingMask=0x5 (binary 101) and fallingMask=0x6 (binary 110), then the first input will generate interrupts on the rising edge, the second input will generate interrupts on the falling edge, the third input will generate interrupts on both rising and falling edges, and all other inputs will not generate interrupts at all.
Generally risingMask and fallingMask will both be 0xFFFFFF, so that all bits generate interrupts on both transitions. However, if an input is changing very rapidly and one does not want interrupts on both or either transition, then that input in the mask should be 0. The msecPoll argument sets the time in milliseconds for polling the inputs. Polling is needed to periodically read inputs that do not generate interrupts on their transitions. An example ipUndig.subsitutions file shows how to load the databases described below.
ipUnidig uses the standard asyn device support. 4 generic databases are provided: IpUnidigBi.db (binary output record), IpUnidigBo.db (binary output record), IpUnidigLi.db (longin record), IpUnidigLo.db (longout record). Database is provided for 3 records, binary output (bo), long input (longin) and binary input (bi). Each of these defines a single record. IpUnidigBi.db, for example contains:
record(bi,"$(P)$(R)") {
field(PINI, "YES")
field(DTYP,"asynUInt32Digital")
field(INP,"@asynMask($(PORT) 0 $(MASK))DIGITAL_INPUT")
field(SCAN, "$(SCAN)")
field(ZNAM, "Low")
field(ONAM, "High")
}
In addition a remoteShutter.db file is provided for using the IP-Unidig with the APS remote shutter control.
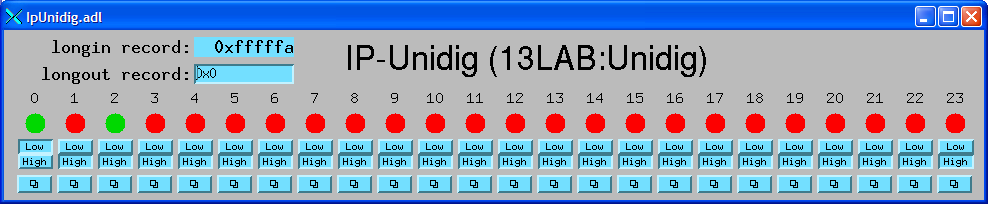
The following show the MEDM screens that are used to control the ipUnidig driver.
ipUnidig.adl is the main screen used to control the ipUndig driver.

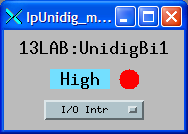
ipUnidig_more.adl can be used to set the scan rate of each bi record.
The IP-Unidig family consists of more than 20 different models. These models differ in the following ways:
The following provides information on specific models. Note that only the IP-Unidig-I and Systran DIO316I have actually been tested. The support for other models is based on reading the manuals. Users who have problems are encouraged to contact the author so that fixes can be incorporated.